Interview with Ashok Kumar Banker

Ashok Kumar Banker began writing stories at the age of nine. He is the author of over seventy books, including the internationally acclaimed Ramayana Series and the recent Burnt Empire Series which is published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt in USA and in the sub-continent by Simon and Schuster India. Ashok Banker’s works have all been bestsellers in India, and have been published around the world. He lives in Los Angeles and Mumbai. He has returned to the genre with which he first made his publishing debut – children’s fiction – with his first chapter book series released by Scholastic India. It is called the Secret School Mysteries. The first story called The Invisible Spy was released in July 2019. The second story in the series arc is called Aliens Ate My Homework! It is slated for release in early 2020.

- The Invisible Spy is a far cry from your mythological stories that you are better known for. So why venture into children’s publishing? Also why did you choose to tell a school story and not retellings of mythology?
It’s actually the other way around. I started my career as a children’s book author and only ventured into mythology much later. As the headnote above says, I began writing at the age of 9. Now, that may seem like childish scribbles, but that’s when I became serious about writing as a vocation. I started my first novel at that age. It would be considered a children’s book today and was several times the length of The Invisible Spy. I never completed it because it was too ambitious and I had bitten off more than I could chew. It was titled Childworld and was about a plane full of children that crash on an island and learn that all the adults in the world have mysteriously died of an unknown virus, and only the children are left alive. I was reading my way through the classics at the time and William Golding’s Lord of the Flies was a powerful influence. Today, looking back across the distance of five decades I would describe it as Lord of the Flies meets Lost meets The Stand.
I never finished Childworld but I continued writing stories (and poems and essays and novels) at feverish speed, filling dozens of ledger books with small cramped handwriting. (Ledger books were the biggest blank notebooks I could find, and I wrote small to make maximum use of the space.) I was recently contacted by an old neighbour from that time, Bianca, who now lives in Canada, and she told me that she remembered me sitting at the dining table in my grandmother’s house filling page after page, completely intent on the task. That was when I was ten. Almost five decades later, I’m still writing.
I wrote at least one book-length work every single year from the age of nine, several books – and stories, poems, songs, essays, scripts – and the vast majority of them were what would be classified as children’s books. I didn’t work up the confidence to actually start sending them out to publishers till I was 15, at which point, I would carry the manuscript of my science fiction YA trilogy (The Man Machine, The Ultimatum, The Last of the Robots) to publisher’s offices in Mumbai, in the hope of getting someone to read my work.
I was a published poet by that time – I published a lot of poetry in my teen years, in journals ranging from Jayanta Mahapatra’s Chandrabhaga in Bhubhaneswarto Menke Katz’s Bitterroot in New York, was interviewed on AIR and other outlets. When I was around 19, Doordarshan Mumbai even did a half hour interview-based feature showcasing my work as one of the youngest emerging poets in the country. I was published at the age of 14 and was a regular contributor to the children’s section of almost every newspaper and magazine that would take my work, from Illustrated Weekly to Evening News, The Afternoon, Free Press Journal, JS, and I don’t even remember all the other names now. I also self-published my first book of poems Ashes in the Dust of Time and it was selected to represent Young India at the World Book Fair in Paris, France, that year. There’s probably copies of it in the National Archive, Asiatic Society, and elsewhere. I had some wonderfully encouraging rejection letters from TLS, The Atlantic Review, and New Yorker. (I also never stopped writing poetry, by the way, and am planning to start sending out some of my more recent works to literary journals here in the US soon.)
Anyway, coming back to my children’s books. I found the addresses of Indian publishers and wrote to them. The first and only one to reply was Zamir Ansari of Penguin Books India. It was basically just a distribution office back then and I think he was the only employee. He was kind enough to meet me on a trip to Mumbai and was the first, and one of the kindest, people I ever met in Indian publishing. You can imagine a teenager in school uniform (I would take off my school tie and my Headboy badges in the hope that I would look older than my age, which I did – I looked mature enough to be allowed into The Exorcist when I was 13), sitting in the coffee shop of The Oberoi with this elderly gentleman, discussing publishing. I had done my homework, spending hours in the USIS and British Council Library, reading every book on publishing, every copy of Bookseller and he must have been impressed by me. He didn’t read my manuscript but he gave me some insights into Indian publishing.
Anyway, I persevered, still writing at least one children’s book and one novel every year, and eventually in my 20s, I finally got accepted by a small imprint called Better Yourself Books. It was the children’s imprint of the Daughters of St. Paul, also known as the Pauline Sisters, and my editor was a wonderful nun named Sister Nivedita. She offered me a small advance and they published what was my first fiction book, Amazing Adventure at Chotta Sheher. It sold over 10,000 copies, which in the 1990s was a huge number, and went in for reprints. I received royalties from it which was more than I ever expected.
I also adapted it to a feature film and it won a prize for the Best Children’s Film Script from the CFSI (Children’s Film Society of India). I was invited to a meeting with the jury, headed by chairperson Shabana Azmi, and I earned even more money for the adaptation rights. (I was already working in advertising as a copywriter, quite successfully, and writing scripts for some of the earliest TV shows such as Saanp Seedi and docudramas, winning a number of awards in both advertising and scriptwriting and making a decent living.) The film never did get made but it was such a zany, fun book that I wish I had a copy to see if it holds up even today.
(One of my quirks is that I never keep copies of my own books, I give them all away. I always believe that I can write much better and keeping my work around seems like an exercise in vanity. I also give away the books I buy to read, since I believe books should be passed on, not hoarded.)
By that time, Penguin had started local publishing headed by David Davidar, and he published another children’s book by me under the Puffin India imprint. It was titled The Missing Parents Mystery and while it was just as much fun as my earlier book, they simply couldn’t sell any of their titles in the market. I began my career as a children’s book author, and the mythological books, while great fun to write, comprise only about a small part of my total output as a writer. So, in a sense, I never really stopped writing children’s books.
Then I met my editor at Pan Macmillan India, Sushmita Chatterjee. Later Sushmita joined Scholastic who then commissioned a chapter book series — the Secret School Mysteries. The first three titles are The Invisible Spy, Aliens Ate My Homework, and The Haunted Centre.
Now, for some unknown reason, the dam seems to have broken.
I have picture books coming out from Lantana Publishing (I Am Brown, illustrated by the amazing Sandhya Prabhat) coming in March 2020, Tiny Tiger to be illustrated by Sandhya’s sister Chhaya Prabhat coming in late 2020, a baby book series called Superzeroes illustrated by Abhijeet Kini coming in late 2020/early 2021, graphic novel adaptations of my Ramayana Series from Campfire Graphic Novels starting with Prince of Ayodhya coming in September 2019, a graphic novel YA series on Shiva starting with The Legend of Rudra coming in October 2019, a YA graphic novel on the Gita in early 2020, an adventure series featuring an SC/ST protagonist called Bhumia Adventures from Tulika, a YA version of the Ramayana from Speaking Tiger, an original middle grade fantasy adventure series starting with Pax Gandhi, Sorceror Supreme, also from Speaking Tiger, and much much more. And those are only my children’s books, of course.
And I’m only getting started. As you can see, I have a lot of lost years to make up for! Besides, I LOVE writing and few books give me as much pleasure as a zany, fun children’s story. So expect many more. 🙂
2. What is your writing routine? How many words can you get done in a day?
Oh, I don’t write every day. In fact, I don’t write most days. I never have a word target. You see, I have a problem of too much focus. I’m the kind of person who could write in a war zone. (I speak from experience, having written an entire book while reporting from Kargil in 1999 for Sunday Mid-Day and Rediff.com.) I have to be careful not to let myself get sucked into writing otherwise you would find me someday, with a miles long beard, filling my 100th Terabyte sized hard disk! I spend most of my reading, day dreaming, exercising, with my family. My wife and I take care of our grand-daughter Leia most days of the week, and she loves to read too. I take a very long time to live with a book and story before setting fingers to keypad, so when I do sit to write, it comes out fully formed. When you read a book or story by me, you are reading the result of several decades of gestation and several hours of actual writing. I’ll talk more about this when answering your other questions below.
3. You are a phenomenally well-read and an eclectic reader. So do you have a reading routine? What format do you prefer reading — print or digital (eBooks/audio)? In fact, any tips on what makes an individual a reader?
It’s kind of you to say so. I read for pleasure, and am lucky (as well as unlucky) that I have such variegated reading interests. I think I actually read about 50 books a month, but that doesn’t include old favourites I dip into now and then, books I reference for my work, and books I start but don’t care to finish. It includes children’s books, which I love because they’re pure story vehicles. I prefer to read in print, hardcover ideally. (Thanks to the incredible library system here in the US, I’m able to indulge my love for reading like never before, ordering as many new hardcovers as I wish, all free. It’s a miracle!) But I also love to listen to audiobooks – also available here free through the library apps. I listen to audiobooks in the morning, while checking my email, cooking my breakfast, eating, and before I sit down to work. Later in the day, I’ll read a print book. And that doesn’t include the picture books I read with Leia.
Speaking for myself, I think growing up in a house full of books (my mother, grandmother, and grandfather were all avid readers) makes a huge difference. Books and reading are like blood and oxygen. You can’t get one without the other. Even as a parent, I was the first one in the house to get hooked on Harry Potter, Twilight, The Hunger Games, you name it. I would buy those books, read them and leave them for my children to discover. They would ignore them or pass them off as “Dad’s latest obsession” until suddenly one day, years later, all their friends were talking about the book and they would come to me and say “Dad, where’s that Harry Potter book?” I was one of the first people in India to register for an internet account and I spent almost all my time (and still do) browsing for books! I think it’s something in your blood.
Leia, as you can see, is fascinated by all my bookshelves and by seeing me reading all the time. But she loves looking at books and being read to, and I have no doubt that she will grow up with books as part of her eco-system. It also helps that almost all my children’s books are dedicated to her!
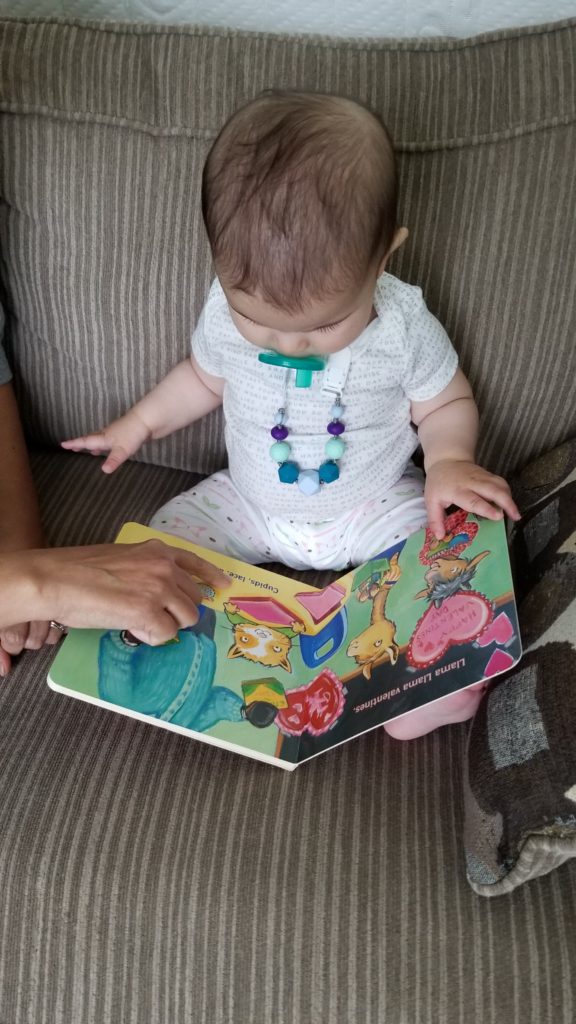

(Picture used with permission of her parents and grandparents.)
4. This year is a first for you in many ways — many new book releases, spanning age groups and spanning continents. If the publications originate on different continents, does it inform your writing style, bearing in mind that you may be writing for slightly different sets of readers who perhaps different expectations?
Oh yes, it changes completely. American editors have a completely different attitude. In India, editors still consider a book to be the author’s work. Children’s book authors here, by and large with a few famous exceptions, are essentially delivering what’s acceptable to their editors.
For instance, we have a wonderful boom in Indian’s children publishing right now, with such amazing books such as the h0le series from Duckbill, books like A Firefly in the Dark by Shazaf Fatima Haider, Calling Muskaan by Himanjali Sarkar, Jwala Kumar and the Gift of Fire by Hansda Sowvendra Shekhar, Amra and the Witch by Arefa Tehsin, The Hidden Children by Reshma Barshikar, to name just a few.
Yet, they’re all incredible, amazing books. In the US. I’m incredibly lucky to have found a great editor in John Joseph Adams, and publisher in Bruce Nichols. Having said that, as I said, I’ve had a little luck and somehow managed to slip one through the cracks. The critical and reader response is wonderful and universally laudatory. The book is doing well and I’m very happy with my editor and publisher.
5. How do you work upon a series arc? Does the plot take shape as you write it or do you create an outline beforehand?
I simply daydream about it. Over time, it all coalesces in my head. It just comes together somehow. I accumulate details, characters, writing styles, structure, all in my mind, and one day, I feel the urge to sit down and “write a little”, and it all comes out in a torrent, pretty much fully formed. It’s a gift from an unknown place and I don’t question or analyse it. I simply accept it with grace and piety.
6. Writing three different kinds of series arcs — chapter books, retelling of the Mahabharata and a yalit trilogy based on Indian mythology — must require a fair amount of mental agility. How do you keep track of all the story plots? Do you make extensive notes?
I read. At some point, a story comes along. It’s all somewhere in my head. I generally have several dozen going at the same time, and I have no idea how I keep track of them all. I just do. No notebooks, no computer files full of notes, no assistants, secretaries, nothing. Just me and my laptop. Sometimes I write. Mostly, I read. Always, I dream.
7. Has dividing your time living in Mumbai and Los Angeles changed your perspective on writing or is context immaterial to your writing?
Living in America makes it easier to see India in a different perspective. I’m finally approaching the completion of a literary novel set in Mumbai which I first started almost 40 years ago. It’s called The Pasha of Pedder Road and is one of those mammoth realistic literary novels that I aspired to write as a young author, but never had the life-experience to attempt. Ironically, or perhaps fittingly, I had to leave Mumbai (where I was born, grew up and lived for 51 years) before I could write about Mumbai again. On the other hand, I no longer feel the slightest bit interested in writing about the US.
8. How/ where do you find ideas for your stories?
Oh, I could never find them. They always find me. I believe there’s a Human Directory that’s secretly handed around by the Story community. My name must feature right at the top, since my first and last names are A and B. So they constantly come calling, at all hours of the day. I often have to pretend I’m not home, otherwise I’d never get any sleep or rest!
9. How did you come up with these five delightful characters — Google baba Peter, gamer Sania, identical twins Usha & Asha, and aspiring scientist Arun? When creating characters, do you work on their backstory or is it sufficient to see them develop as the story moves ahead? (I am always curious whether the character comes first or the plot or is it a bit of both and then it evolves.)
Good question. I wish I had the answer. As I said, I simply write the whole thing. All fully formed. More or less the way you read it. When I hold a copy of one of my books in my hand, I read it and it’s all just as new to me as it is to you. I remember these words passing from my mind to the screen, but have no clue how they came to be there. As Erica Jong once wrote: “We write as leaves breathe: to live.” I simply breathe, and the air comes out as perfectly shaped stories, characters and all.
10. It is early days as yet but do you have any idea what is the response, particularly amongst children, to Invisible Spy?
It’s my first book ever to receive five star reviews, and to be loved by everyone who reads it. The response is overwhelming. I think for the first time in my 72-book career I have a book that’s universally loved. It is a wonderful feeling!
11. Who are the writers you admire and may have influenced your writing as well?
They change every few days. I read so much, it’s like pointing to one fish in the ocean and say, that one. It’s gone almost instantly, and then there’s another, and another. Hundreds. Thousands even. More than writers, it’s individual books. Often, I pick up a book at random in a library and if I like the first page, I keep reading. I may not even look at the title or author name until much later. I’ve often thought I would prefer that my books be published without my name mentioned anywhere. After all, all art is ultimately a collective creative experience. It takes a village to create a story. A writer merely jots it down.
12. Do you have any all-time favourite stories? Does this list change over time?
Too many to count or name. Ever changing, ever expanding list. A monster with a bottomless appetite, that’s me as a reader! As a young kid, I used to read my way through entire circulating libraries. I can devour whole series like guzzling water. Books are life to me.
Thank you for these wonderful questions!
Happy Reading!
Ashok Kumar Banker
Los Angeles, July 2019
21 August 2019